Here’s What You Should Know about Testosterone Production
 Testosterone is important as it maintains our physical strength, our focus, and our mood, but do you an idea about testosterone production? How is it made?
Testosterone is important as it maintains our physical strength, our focus, and our mood, but do you an idea about testosterone production? How is it made?
It’s not just an academic question. An understanding of how our bodies produce testosterone leads to an understanding of what might cause our bodies to stop producing enough of the stuff, and understanding a problem is the first step to solving it.
Testosterone Production 101 – The Three Types of Testosterone
In essence, testosterone is a steroid hormone. The changes and benefits it triggers in the body are detailed right over here. The average male human creates 7mg of testosterone per day, but there are actually three different types. Not all of it is usable by the body, or at least not to produce the effects you’re probably looking for.
 Free Testosterone
Free Testosterone
Free testosterone is so named because it has no attached proteins. It’s free to float through the bloodstream, and isn’t bonded to any other molecules. Free testosterone is the type of testosterone that has all those great physical and mental benefits, because it’s able to roam our bodies and activate receptors in various cells. Even though this is the kind of testosterone we think of as the most beneficial, it has the smallest concentration of the three. It only comprises about 2%-3% of our total testosterone levels. Everything we do for testosterone production is really meant to increase free testosterone, but the best way to do that is to raise our overall levels.
 SHBG-Bound Testosterone
SHBG-Bound Testosterone
This type of the male hormone makes up about 40%-50% of our total testosterone levels. It’s bound to SHBG (sex hormone-binding-globulin), which is a protein produced in the liver. It regulates the amount of free testosterone in the body. SHBG-Bound Testosterone is what’s known as “biologically inactive”, meaning it doesn’t actually have any other effect in our bodies beyond helping regulate our total levels. This type of T doesn’t have harmful effects either, but it is why a man might test with adequately high testosterone levels but still experience the symptoms of testosterone deficiency.
 Albumin-Bound Testosterone
Albumin-Bound Testosterone
This makes up the remainder of our total testosterone. It’s bound to the protein albumin, which is also produced in the liver. Its function is to stabilize fluid volumes between our cells. Albumin-Bound Testosterone is also biologically inactive, but unlike the SHBG-Bound variety, its bond can be broken. That converts it back into free testosterone, making the stuff sort of testosterone reserve supply.
About 95% of our testosterone is produced in the testicles. The rest is made in our adrenal glands, which is why the hormone is present in women as well. For men, though, it’s almost entirely the testicles.
It’s a pretty complex process that results in the male hormone. Learn about testosterone production in this basic rundown:
 The hypothalamus (part of the brain) secretes gonadotropin-releasing hormone. This stuff loops around to the back of the brain and hits the pituitary gland.
The hypothalamus (part of the brain) secretes gonadotropin-releasing hormone. This stuff loops around to the back of the brain and hits the pituitary gland.
 The pituitary gland receives the gonadotropin-releasing hormone, and responds by producing two more hormones. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Both of these natural chemicals enter the bloodstream and make their way to the testicles.
The pituitary gland receives the gonadotropin-releasing hormone, and responds by producing two more hormones. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Both of these natural chemicals enter the bloodstream and make their way to the testicles.
 Once they’ve arrived down there, the FSH and LH do two different things. FSH initiates sperm production (important!), while LH kicks off testosterone production (just as important!)
Once they’ve arrived down there, the FSH and LH do two different things. FSH initiates sperm production (important!), while LH kicks off testosterone production (just as important!)
 The actual cells that create the testosterone are called Leydig cells. They work by converting cholesterol into testosterone. That cholesterol literally comes from the bloodstream, which is why a healthy level of T can actually improve your heart health. It’s also the reason eating eggs is so beneficial to testosterone levels!
The actual cells that create the testosterone are called Leydig cells. They work by converting cholesterol into testosterone. That cholesterol literally comes from the bloodstream, which is why a healthy level of T can actually improve your heart health. It’s also the reason eating eggs is so beneficial to testosterone levels!
 During testosterone production, it’s released by the testicles into the bloodstream. Most of the stuff attaches to SHBG and albumin, nullifying its effects. It’s the small amount that remains free that aids our strength, focus, sexual drive, and all the other great benefits of testosterone.
During testosterone production, it’s released by the testicles into the bloodstream. Most of the stuff attaches to SHBG and albumin, nullifying its effects. It’s the small amount that remains free that aids our strength, focus, sexual drive, and all the other great benefits of testosterone.
Here’s a handy chart of the HPA-axis:
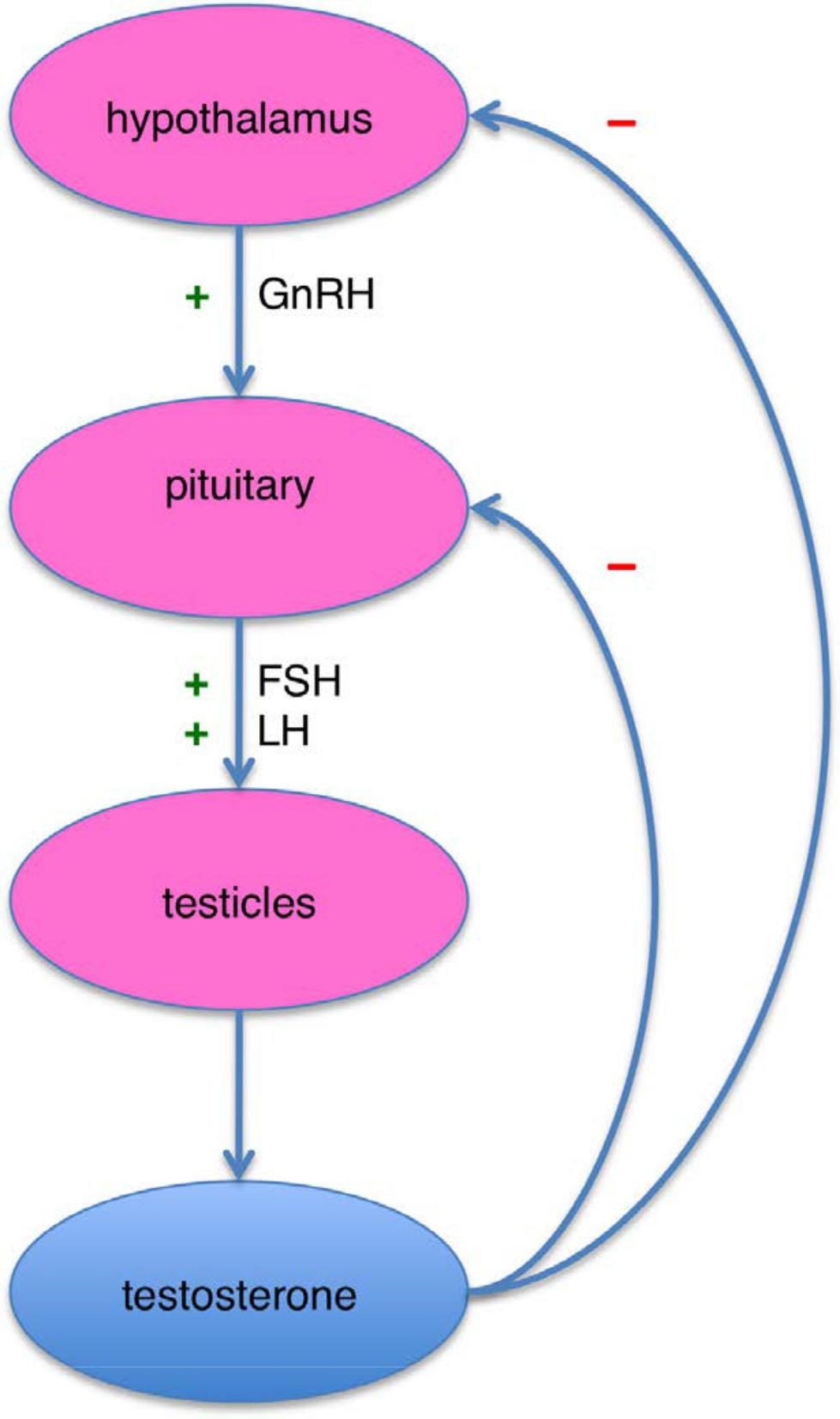
Image source: Wikipedia
In essence, testosterone is a steroid hormone. The changes and benefits it triggers in the body are detailed right over here. The average male human creates 7mg of testosterone per day, but there are actually three different types. Not all of it is usable by the body, or at least not to produce the effects you’re probably looking for.
Hormone Therapeutics aims to help people looking to improve and optimize their health through natural means or through the guidance of our physicians.
Don’t miss out our free weekly tips and news on Low T, hormone balancing, healthy living, nutrition and a lot more.
Want more?

Sign up today and Get our ebook, ‘Naturally Increase Your Testosterone Levels’ absolutely FREE.
Here’s What You Should Know about Testosterone Production
Saleamp Design November 4th, 2016
Posted In: Low T Info
Tags: albumin, biologically available, Follicle Stimulating Hormone, free testosterone, FSH, GnRH, growth hormone, HPA axis, hypothalamus, LH, low t, Luteinizing Hormone, pituitary, sex hormone-binding-globulin, SHBG, testicles, testosterone, testosterone levels, testosterone production


 Free Testosterone
Free Testosterone SHBG-Bound Testosterone
SHBG-Bound Testosterone Albumin-Bound Testosterone
Albumin-Bound Testosterone